二叉搜索树中序后代
二叉树的中序后代是二叉树中序遍历中下一个节点。所以,对于树内的最后一个节点来说,它是 NULL。由于二叉搜索树的中序遍历是一个排序数组。比给定节点大键最小的节点被定义为它的中序后代。在 BST 中,中序后代有两种可能,即在节点的右侧子树或祖先中,值最小的节点。否则,该节点的中序后代不存在。
BST 算法中的中序后代算法
- 如果
root=NULL,则将succ设为NULL并返回。 - 如果
root->data<current->data,则succ为current,current为current->left。 - 如果
root->data>current->data,则current为current->right。 - 如果
root->data==current->data和root->right!=NULL,succ=minimum(current->right)。 - 返回
succ。
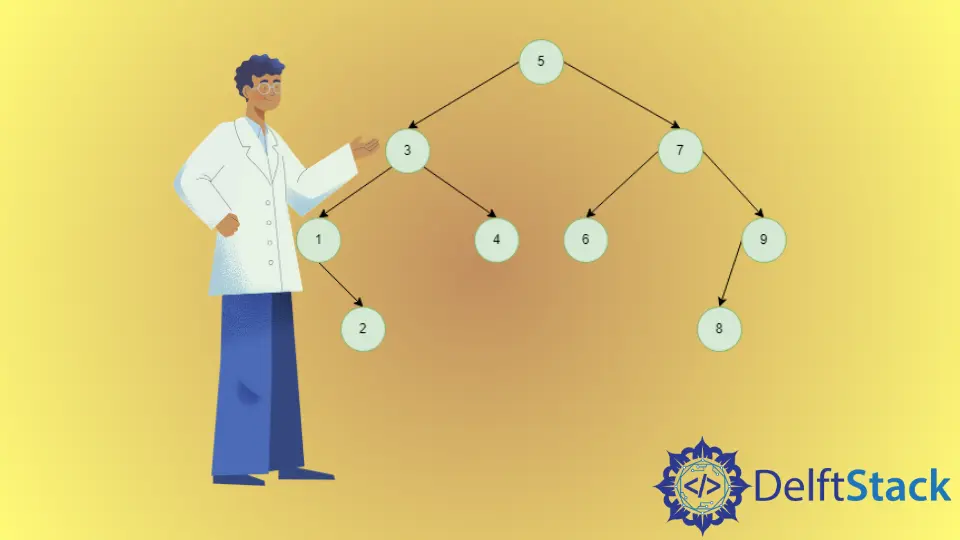
BST 中的中序后代图示
3 的中序后代是 4,因为 3 有一个右结点,4 是右子树中比 3 大的最小的结点。
4 的顺序后代是 5,因为 4 没有右结点,我们要看它的祖先,其中 5 是比 4 大的最小的结点。
BST 中序后代的实现
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Node {
public:
int data;
Node *left, *right;
Node(int x) {
this->data = x;
this->left = this->right = NULL;
}
};
Node* insert(Node* root, int key) {
if (root == NULL) {
return new Node(key);
}
if (key < root->data) {
root->left = insert(root->left, key);
} else {
root->right = insert(root->right, key);
}
return root;
}
Node* getNextleft(Node* root) {
while (root->left) {
root = root->left;
}
return root;
}
void inorderSuccessor(Node* root, Node*& succ, int key) {
if (root == NULL) {
succ = NULL;
return;
}
if (root->data == key) {
if (root->right) {
succ = getNextleft(root->right);
}
}
else if (key < root->data) {
succ = root;
inorderSuccessor(root->left, succ, key);
} else {
inorderSuccessor(root->right, succ, key);
}
}
int main() {
int keys[] = {1, 5, 8, 2, 6, 3, 7, 4};
Node* root = NULL;
for (int key : keys) {
root = insert(root, key);
}
for (int key : keys) {
Node* prec = NULL;
inorderSuccessor(root, prec, key);
if (prec) {
cout << "Inorder successor of node " << key << " is " << prec->data;
} else {
cout << "No inorder Successor of node " << key;
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
BST 查找中序后代的算法复杂度
时间复杂度
- 平均情况
在平均情况下,在 BST 中寻找中序后代的时间复杂度与二叉搜索树的高度相当。平均来说,一个 BST 的高度是 O(logn)。当形成的 BST 是一个平衡的 BST 时,就会出现这种情况。因此,时间复杂度是 [Big Theta]:O(logn)。
- 最佳情况
最好的情况是当树是一个平衡的 BST 时。最佳情况下,删除的时间复杂度为 O(logn)。它与平均情况下的时间复杂度相同。
- 最坏情况
在最坏的情况下,我们可能需要从根节点到最深的叶子节点,即树的整个高度 h。如果树是不平衡的,即它是倾斜的,树的高度可能会变成 n,因此插入和搜索操作的最坏情况下的时间复杂性是 O(n)。
空间复杂度
由于递归调用所需的额外空间,该算法的空间复杂度为 O(h)。
Harshit Jindal has done his Bachelors in Computer Science Engineering(2021) from DTU. He has always been a problem solver and now turned that into his profession. Currently working at M365 Cloud Security team(Torus) on Cloud Security Services and Datacenter Buildout Automation.
LinkedIn
