如何快速检查 Python 列表中是否存在特定值
我们将介绍不同的方法来检查 Python 列表中是否存在特定值并比较它们的性能。
这些方法包括
- 成员资格检查方法-
in方法来检查值是否存在 - 将列表转换为
set,然后使用成员资格检查方法in
in 检查 Python 列表中值是否存在的方法
in 是在 Python 列表、集合、字典或其他可迭代的 Python 对象中执行成员资格检查的正确方法。
>>> testList = [1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> 2 in testList
True
>>> 6 in testList
False
在 Python 中将列表转换为集合 set,然后进行成员资格检查
如果列表长度增加,则列表成员资格检查可能效率不高,尤其是如果列表中存在重复元素。
在这种情况下,Python 集合 set 是进行成员资格检查的更好的数据类型,因为集合中的元素值都是唯一的。
列表和集合成员资格检查之间的性能比较
我们将比较四种情况下的效果差异,
- 原始列表具有唯一值,并且选中的值存在于列表中
- 原始列表具有唯一值,并且列表中不存在检查的值
- 原始列表具有重复的值,并且检查的值存在于列表中
- 原始列表只有重复的值,并且列表中不存在检查的值
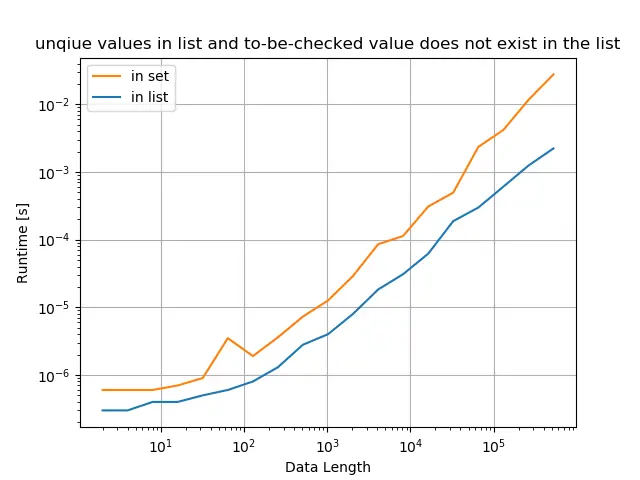
原始列表仅具有唯一值,并且选中的值存在于列表中
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
randomlist = a[: n // 2].tolist()
randomvalue = randomlist[len(randomlist) // 2]
return [randomlist, randomvalue]
def inListMethod(L):
x, y = L
return y in x
def inSetMethod(L):
x, y = L
x = set(x)
return y in x
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
kernels=[inListMethod, inSetMethod],
labels=["in list", "in set"],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(1, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
title="unique values in list and to-be-checked value exists in the list",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
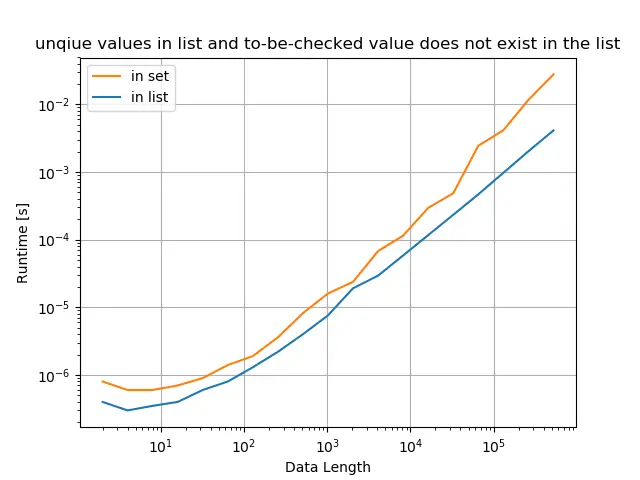
原始列表只有唯一值,并且列表中不存在检查的值
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
randomlist = a[: n // 2].tolist()
randomvalue = n + 1
return [randomlist, randomvalue]
def inListMethod(L):
x, y = L
return y in x
def inSetMethod(L):
x, y = L
x = set(x)
return y in x
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
kernels=[inListMethod, inSetMethod],
labels=["in list", "in set"],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(1, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
title="unique values in list and to-be-checked value does not exist in the list",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
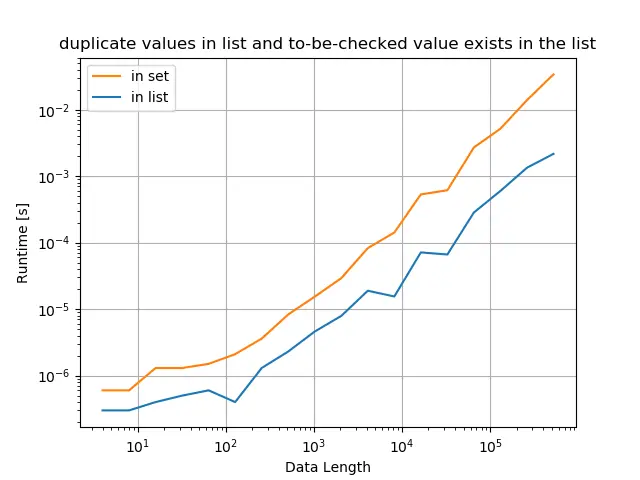
原始列表具有重复的值,并且检查的值存在于列表中
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
randomlist = np.random.choice(n, n // 2).tolist()
randomvalue = randomlist[len(randomlist) // 2]
return [randomlist, randomvalue]
def inListMethod(L):
x, y = L
return y in x
def inSetMethod(L):
x, y = L
x = set(x)
return y in x
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
kernels=[inListMethod, inSetMethod],
labels=["in list", "in set"],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(2, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
title="duplicate values in list and to-be-checked value exists in the list",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
原始列表只有重复的值,并且列表中不存在检查的值
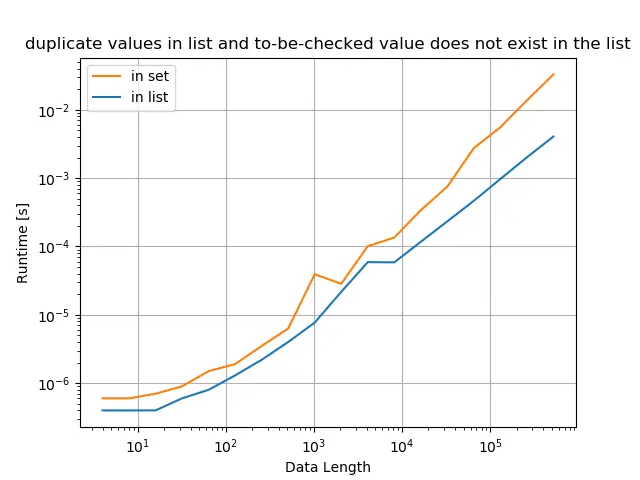
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
randomlist = np.random.choice(n, n // 2).tolist()
randomvalue = n + 1
return [randomlist, randomvalue]
def inListMethod(L):
x, y = L
return y in x
def inSetMethod(L):
x, y = L
x = set(x)
return y in x
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
kernels=[inListMethod, inSetMethod],
labels=["in list", "in set"],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(2, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
title="duplicate values in list and to-be-checked value does not exist in the list",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
性能效果比较结论
尽管 Python 中的 set 成员资格检查比 Python 列表 list 中的成员资格检查更快,但是从列表 list 进行转换或集合 set 消耗时间。因此,如果给定的数据是 Python 列表,那么如果你首先将列表转换为 set,然后执行 set 成员资格检入,则不会带来任何性能上的好处。
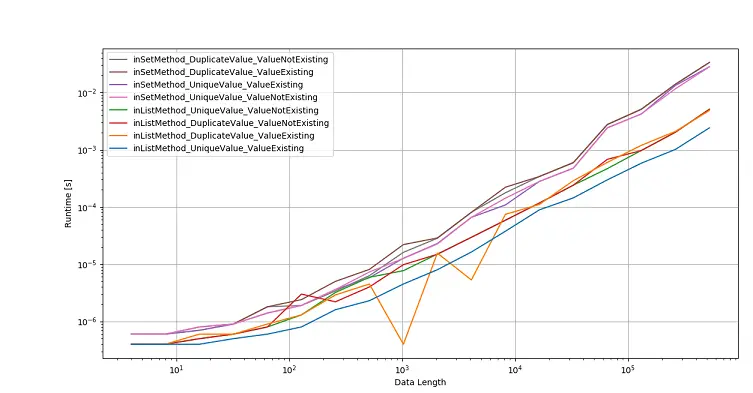
from itertools import chain
import perfplot
import numpy as np
def setupTest(n):
a = np.arange(n)
np.random.shuffle(a)
unique_randomlist = a[: n // 2].tolist()
duplicate_randomlist = np.random.choice(n, n // 2).tolist()
existing_randomvalue = unique_randomlist[len(unique_randomlist) // 2]
nonexisting_randomvalue = n + 1
return [
unique_randomlist,
duplicate_randomlist,
existing_randomvalue,
nonexisting_randomvalue,
]
def inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
return ex in u
def inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
return ex in d
def inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
return ne in u
def inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
return ne in d
def inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
u = set(u)
return ex in u
def inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
d = set(d)
return ex in d
def inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
u = set(u)
return ne in u
def inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting(L):
u, d, ex, ne = L
d = set(d)
return ne in d
perfplot.show(
setup=setupTest,
equality_check=None,
kernels=[
inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting,
inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting,
inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting,
inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting,
inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting,
inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting,
inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting,
inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting,
],
labels=[
"inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting",
"inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting",
"inListMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting",
"inListMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting",
"inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueExisting",
"inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueExisting",
"inSetMethod_UniqueValue_ValueNotExisting",
"inSetMethod_DuplicateValue_ValueNotExisting",
],
n_range=[2 ** k for k in range(2, 20)],
xlabel="Data Length",
logx=True,
logy=True,
)
Founder of DelftStack.com. Jinku has worked in the robotics and automotive industries for over 8 years. He sharpened his coding skills when he needed to do the automatic testing, data collection from remote servers and report creation from the endurance test. He is from an electrical/electronics engineering background but has expanded his interest to embedded electronics, embedded programming and front-/back-end programming.
LinkedIn