Python 中的图数据结构
在编程中,图数据结构表示一组相互关联的对象。每个对象都称为顶点,链接称为边。
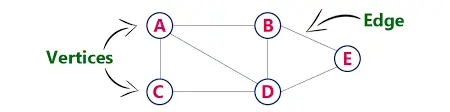
上图中,{A, B, C, D, E} 是顶点,集合用 V 符号表示。边的集合用 E 表示,在上面的例子中它是 {ad,ac,ab,cd,bd,be,de}。
我们可以根据不同的标准对图表进行分类。首先,我们有基于方向的图。
这些是无向图和有向图。在无向图中,边没有方向。
这意味着边 ab 与 ba 相同。对于每条边都有方向或方向的有向图则相反。
基于权重,我们有加权图和非加权图。加权图有一些与边相关的值。
还有一些特殊的图,如树、有向无环图等。由于它们的非线性特性,图在现实世界中有很多应用。
谷歌地图在他们的交通系统中使用图表,甚至 Facebook 也使用图表来可视化用户及其朋友列表。
在本教程中,我们将讨论用 Python 表示一个简单的图形。
在 Python 中使用邻接表实现图
邻接列表存储每个顶点及其相邻顶点以可视化图形。这可以使用字典来表示。
每个顶点都将是字典的键,键的对应值将包含列表中的相邻顶点。
adjacency_lst = {}
mylst = []
def graph_node(node):
if node not in mylst:
mylst.append(node)
else:
print("The given node exists")
def graph_edge(node1, node2):
temp = []
if node1 in mylst and node2 in mylst:
if node1 not in adjacency_lst:
temp.append(node2)
adjacency_lst[node1] = temp
elif node1 in adjacency_lst:
temp.extend(adjacency_lst[node1])
temp.append(node2)
adjacency_lst[node1] = temp
else:
print("The given node does not exist")
def disp_graph():
for node in adjacency_lst:
print(node, " -> ", [i for i in adjacency_lst[node]])
graph_node("a")
graph_node("b")
graph_node("c")
graph_node("d")
graph_edge("a", "b")
graph_edge("b", "c")
graph_edge("c", "d")
graph_edge("d", "a")
disp_graph()
print(adjacency_lst)
输出:
a -> ['b']
b -> ['c']
c -> ['d']
d -> ['a']
{'a': ['b'], 'b': ['c'], 'c': ['d'], 'd': ['a']}
我们使用上面例子中的邻接表来实现一个简单的图。一开始,定义了 adjacency_lst 字典来存储节点和边。
graph_node() 函数将一个顶点添加到该字典并检查一个节点是否已经存在。我们使用 graph_edge() 函数添加边。
disp_graph() 函数通过显示节点的边缘来显示此图。
在 Python 中使用邻接矩阵实现图
我们可以使用矩阵来表示图。矩阵是二维数组。
在邻接矩阵中,特定行和列的值表示是否存在边。
如果 A[i][j] 为 0,则 i 和 j 之间没有边。值为 1 表示边缘存在。
def graph_node(v):
global graph
global nodes_no
global nodes
if v in nodes:
print("Node already exists")
else:
nodes_no = nodes_no + 1
nodes.append(v)
if nodes_no > 1:
for vertex in graph:
vertex.append(0)
temp = []
for i in range(nodes_no):
temp.append(0)
graph.append(temp)
def graph_edge(v1, v2, e):
global graph
global nodes_no
global nodes
if v1 not in nodes:
print("Node ", v1, " does not exist.")
elif v2 not in nodes:
print("Node ", v2, " does not exist.")
else:
index1 = nodes.index(v1)
index2 = nodes.index(v2)
graph[index1][index2] = e
def disp_graph():
global graph
global nodes_no
for i in range(nodes_no):
for j in range(nodes_no):
if graph[i][j] != 0:
print(nodes[i], " -> ", nodes[j], "Weight for the edge: ", graph[i][j])
nodes = []
nodes_no = 0
graph = []
graph_node(1)
graph_node(2)
graph_node(3)
graph_node(4)
graph_edge(1, 2, 1)
graph_edge(1, 3, 1)
graph_edge(2, 3, 0)
graph_edge(3, 1, 2)
disp_graph()
print("Matrix Representation: ", graph)
输出:
1 -> 2 Weight for the edge: 1
1 -> 3 Weight for the edge: 1
3 -> 1 Weight for the edge: 2
Matrix Representation: [[0, 1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [2, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0]]
在上面的例子中,我们使用邻接矩阵实现了一个图。我们维护图是一个名为 graph 的列表列表。
graph_node() 函数向图中添加一个顶点,并添加顶点之间的边。
使用 graph_edge() 函数。disp_graph() 显示矩阵中节点和边的表示。
Manav is a IT Professional who has a lot of experience as a core developer in many live projects. He is an avid learner who enjoys learning new things and sharing his findings whenever possible.
LinkedIn