Tkinter 线程
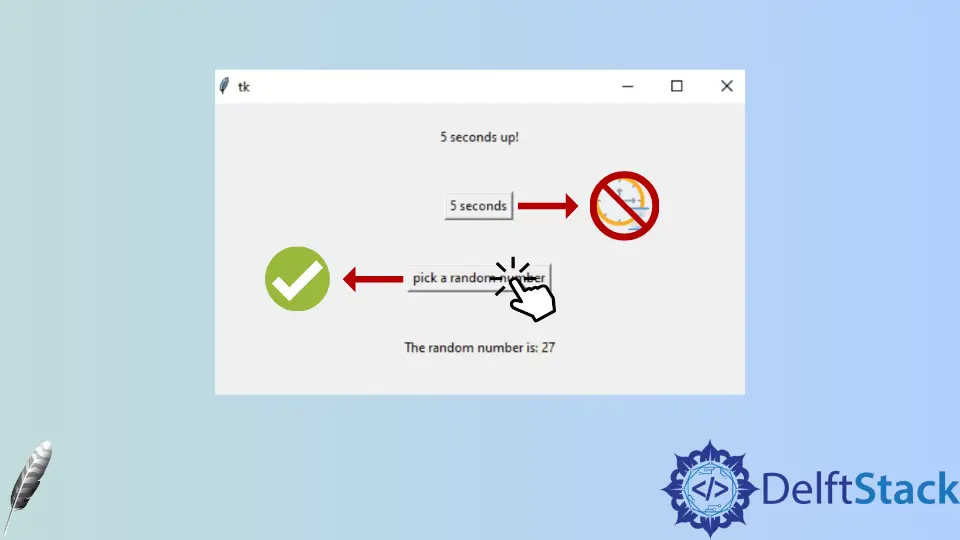
本教程展示了如何在 Tkinter 中处理单线程和多线程。
在 Tkinter 中处理单线程
Python 提供了许多用于创建 GUI(图形用户界面)的选项。在所有的 GUI 模块中,Tkinter 是使用最广泛的。
Tkinter 模块是在 Python 中创建 GUI 应用程序的最佳且简单的方法。在创建 GUI 时,我们可能需要在后端执行多个任务或操作。
假设我们要同时进行多任务;当我们在执行最后一个任务之前分配下一个任务时,就会出现问题。因为在后端,每一个任务都是一个接一个的执行。
在单个任务期间,GUI 窗口也不会移动,这就是我们需要在 Tkinter 中进行线程化的原因。
不使用 threading 的示例:
from tkinter import *
import time
from random import randint
# Initialize a new window
root = Tk()
root.geometry("500x400")
# A function that interrupts for five seconds
def five_seconds():
time.sleep(5)
label.config(text="5 seconds up!")
# A function that generates a random number
def random_numbers():
rand_label.config(text=f"The random number is: {randint(1,100)}")
label = Label(root, text="Hello there!")
label.pack(pady=20)
# A button that calls a function
button1 = Button(root, text="5 seconds", command=five_seconds)
button1.pack(pady=20)
button2 = Button(root, text="pick a random number", command=random_numbers)
button2.pack(pady=20)
rand_label = Label(root, text="")
rand_label.pack(pady=20)
root.mainloop()
如你所见,如果我们不使用 threading,我们必须等待执行下一个任务。
这样整个程序就卡住了,直到最后一个任务执行完成。
Python 有一个内置的 threading 库来处理这种情况。
import threading
from tkinter import *
import time
from random import randint
# Initialize a new window
root = Tk()
root.geometry("500x400")
# A function that interrupts for five seconds
def five_seconds():
time.sleep(5)
label.config(text="5 seconds up!")
# A function that generates a random number
def random_numbers():
rand_label.config(text=f"The random number is: {randint(1,100)}")
label = Label(root, text="Hello there!")
label.pack(pady=20)
# A button that calls a function
button1 = Button(
root, text="5 seconds", command=threading.Thread(target=five_seconds).start()
)
button1.pack(pady=20)
button2 = Button(root, text="pick a random number", command=random_numbers)
button2.pack(pady=20)
rand_label = Label(root, text="")
rand_label.pack(pady=20)
root.mainloop()
查看与线程的区别。
button1 = Button(
root, text="5 seconds", command=threading.Thread(target=five_seconds).start()
)
在这行代码中,我们使用了 Thread() 类。
Thread() 类有一个 target 选项,它将函数作为值。start() 方法有助于启动线程。
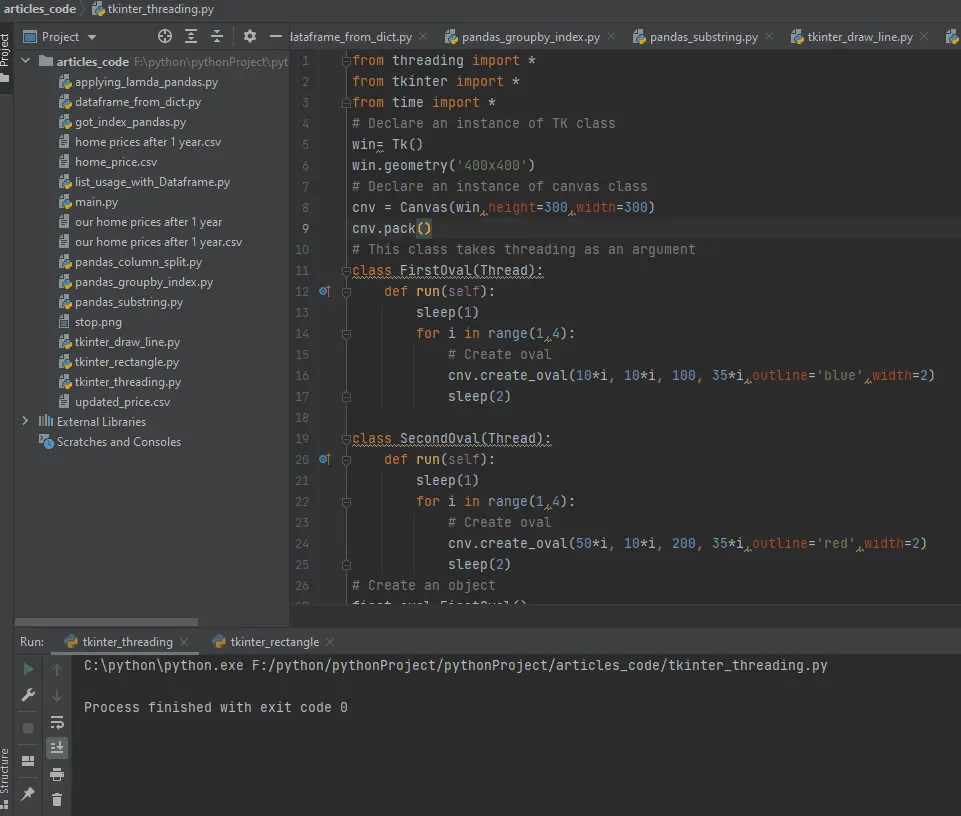
在 Tkinter 中处理多线程
from threading import *
from tkinter import *
from time import *
# Declare an instance of TK class
win = Tk()
win.geometry("400x400")
# Declare an instance of canvas class
cnv = Canvas(win, height=300, width=300)
cnv.pack()
# This class takes threading as an argument
class FirstOval(Thread):
def run(self):
sleep(1)
for i in range(1, 4):
# Create oval
cnv.create_oval(10 * i, 10 * i, 100, 35 * i, outline="blue", width=2)
sleep(2)
class SecondOval(Thread):
def run(self):
sleep(1)
for i in range(1, 4):
# Create oval
cnv.create_oval(50 * i, 10 * i, 200, 35 * i, outline="red", width=2)
sleep(2)
# Create an object
first_oval = FirstOval()
first_oval.start()
second_oval = SecondOval()
second_oval.start()
win.mainloop()
现在我们正在使用多线程。注意 FirstOval 和 SecondOval 类;它们将 Thread 作为参数并在 run() 方法的帮助下同时运行。
run() 方法会自动执行,代码包含在其中。
Hello! I am Salman Bin Mehmood(Baum), a software developer and I help organizations, address complex problems. My expertise lies within back-end, data science and machine learning. I am a lifelong learner, currently working on metaverse, and enrolled in a course building an AI application with python. I love solving problems and developing bug-free software for people. I write content related to python and hot Technologies.
LinkedIn