在 PHP 中绘制图形
本文介绍了如何在 PHP 中使用 pChart 创建图形。第一个是条形图,第二个是样条图,最后一个是来自 MySQL 的直方图。
设置你的环境
在使用 pChart 之前,你首先需要安装 PHP5。你可以从 SourceForge 获得 PHP5 作为 XAMPP 5.5.28 的一部分。
当你有 XAMPP 5.5.28 时,从他们的官方网站下载 pChart。之后,将 pChart 提取到 XAMPP 5.5.28 的 htdocs 文件夹中。
打开 pChart 文件夹,其结构应如下图所示:

注意:
class文件夹包含我们将使用的类定义。fonts文件夹包含我们可以在图表中使用的字体文件。
完成 pChart 设置后,你现在可以开始绘图了。
在 PHP 中使用 pChart 绘制条形图
使用 pChart 绘制条形图的 PHP 代码必须包含 class 文件夹中的三个文件。这些文件是:
pData.class.phppImage.class.phppDraw.class.php
在这些文件中,pData.class.php 允许你加载将在图表中使用的数据。你需要 pDraw.class.php 来绘制图表。
接下来,pImage.class.php 将让你在 Web 浏览器中呈现图表。你必须使用 PHP required_once() 包含这些文件。
你可以使用相对路径包含它们或定义一个 PCART_PATH 常量。然后使用 set_include_path(),你可以为 pChart 类使用短目录名称。
话虽如此,我们可以使用以下步骤创建带有 pChart 的条形图:
-
定义
PCART_PATH常量。 -
使用
set_include_path()作为pChart类的短目录名称。 -
使用
required_once()包含pChart类。 -
创建一个新的
pData对象。 -
创建你的数据或将其导入。
-
使用
addPoints方法将数据添加到pData对象。 -
使用
pImage对象为图表创建图像。 -
设置图表的字体。
-
使用
pData的setGraphArea方法设置图形区域。 -
使用
pData的drawScale和drawBarChart方法绘制刻度和条形图。 -
发送标头信息以告诉浏览器你正在发送图像。
-
使用
pData的Render方法渲染图像。确保将null传递给Render方法。
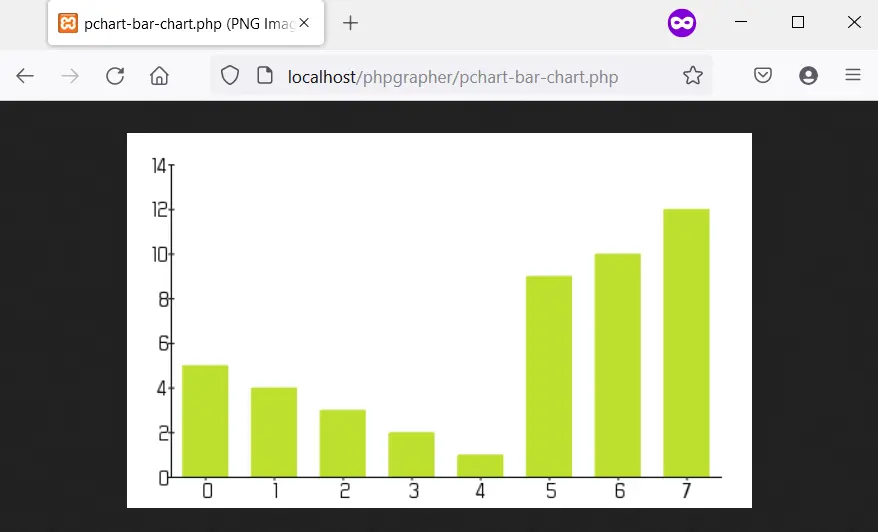
以下是这些步骤的实现。以下是 Firefox 101.0 中的输出图像。
<?php
// The definition of the PCHART_PATH assumes
// you have pChart one directory above your
// current working folder.
define("PCHART_PATH", "../pChart");
set_include_path(get_include_path() . PATH_SEPARATOR . PCHART_PATH);
// Since we have defined the path, and used
// the get_include_path() function, we can
// reference the class folder without writing
// its full path.
require_once "class/pDraw.class.php";
require_once "class/pImage.class.php";
require_once "class/pData.class.php";
// Create the pChart Object
$pchart_data = new pData();
// Some sample data that we'll use to plot
// the bar chart.
$sample_data_set = [5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 9, 10, 12];
$pchart_data->addPoints($sample_data_set);
// Create the pChart Image. The first two argument
// to the pImage object are the width and height
// of the rendered chart.
$pchart_image = new pImage(500, 300, $pchart_data);
// Set the font.
$pchart_image->setFontProperties(
["FontName" => PCHART_PATH . "/fonts/Forgotte.ttf",
"FontSize" => 16]
);
// Define the graph area. The first two arguments
// are the x-coordinates. While the last two are
// the y-coordinates.
$pchart_image->setGraphArea(35, 25, 475, 275);
$pchart_image->drawScale();
$pchart_image->drawBarChart();
// Render the chart as a PNG image
header("Content-Type: image/png");
$pchart_image->Render(null);
?>
输出:
在 PHP 中使用 pChart 绘制样条图
绘制样条图的过程与绘制条形图的过程相同,不同之处在于你使用 drawSplineChart 方法绘制样条图。此外,你可以选择不将图表作为图像发送。
相反,你可以选择 pData 的 Stroke 方法在 Web 浏览器中呈现图表。
以下代码使用 pChart 绘制样条图。此外,我们使用的是 fonts 目录中的 MankSans.ttf 字体。
<?php
// The definition of the PCHART_PATH assumes
// you have pChart one directory above your
// current working folder.
define("PCHART_PATH", "../pChart");
set_include_path(get_include_path() . PATH_SEPARATOR . PCHART_PATH);
// Since we have defined the path, and used
// the get_include_path() function, we can
// reference the class folder without writing
// its full path.
require_once "class/pDraw.class.php";
require_once "class/pImage.class.php";
require_once "class/pData.class.php";
// Create the pChart Object
$pchart_data = new pData();
// Some sample data that we'll use to plot
// the spline chart.
$pchart_data->addPoints([4,2,1,4]);
// Create the pChart Image. The first two argument
// to the pImage object are the width and height
// of the rendered chart.
$pchart_image = new pImage(700, 220, $pchart_data);
// Set the font.
$pchart_image->setFontProperties(
["FontName" => PCHART_PATH . "/fonts/MankSans.ttf",
"FontSize"=> 18]
);
// Define the graph area. The first two arguments
// are the x-coordinates. While the last two are
// the y-coordinates.
$pchart_image->setGraphArea(60, 40, 670, 190);
$pchart_image->drawScale();
$pchart_image->drawSplineChart();
// Draw the chart as a stroke.
$pchart_image->Stroke();
?>
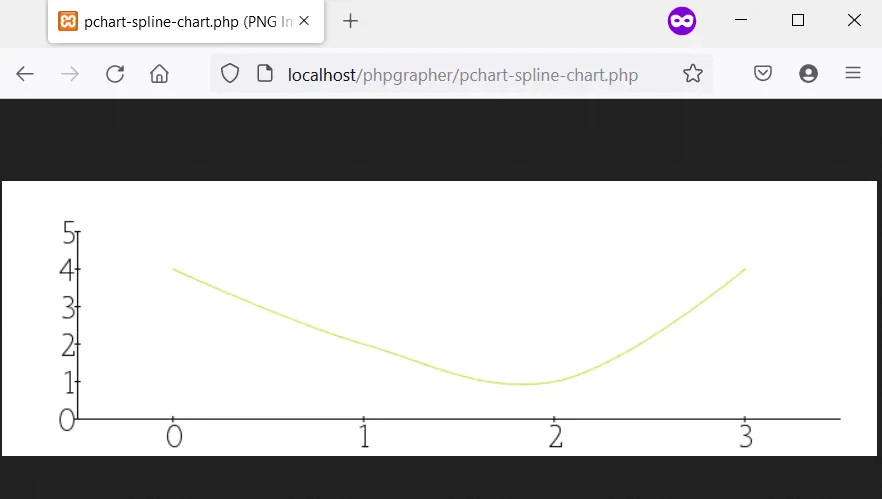
输出:
在 PHP 中从 MySQL 数据库中绘制柱状图
绘制直方图遵循与条形图和样条图类似的步骤。但是,有一些差异值得指出。
首先,直方图的数据将来自 MySQL。这意味着你应该有一个包含一些示例数据的数据库。
其次,你将使用表列名称作为直方图上的轴。为此,你将使用一些 pData 方法,例如 setAbscissa、setSeriesOnAxis 和 setAxisName。
现在,创建一个名为 weather_measurements 的数据库,然后使用以下命令创建一个表:
CREATE TABLE measures (
timestamp INT NOT NULL DEFAULT '0',
temperature INT NOT NULL,
humidity INT NOT NULL
)
使用以下命令将样本数据插入 measures 表中:
INSERT INTO measures (timestamp, temperature, humidity) VALUES (UNIX_TIMESTAMP(), 20, 50);
INSERT INTO measures (timestamp, temperature, humidity) VALUES (UNIX_TIMESTAMP(), 18, 44);
INSERT INTO measures (timestamp, temperature, humidity) VALUES (UNIX_TIMESTAMP(), 19, 70);
确保样本数据在数据库中,然后使用以下命令创建直方图:
<?php
// The definition of the PCHART_PATH assumes
// you have pChart one directory above your
// current working folder.
define("PCHART_PATH", "../pChart");
set_include_path(get_include_path() . PATH_SEPARATOR . PCHART_PATH);
// Since we have defined the path, and used
// the get_include_path() function, we can
// reference the class folder without writing
// its full path.
require_once "class/pDraw.class.php";
require_once "class/pImage.class.php";
require_once "class/pData.class.php";
// Create the pChart Object
$pchart_data = new pData();
// Connect to MySQL
$connect_to_mysql = new mysqli("localhost", "root", "", "weather_measurements");
// query the database and get the result
$query_the_table = "SELECT * FROM measures";
$mysql_result = mysqli_query($connect_to_mysql, $query_the_table);
// Declare the variables for the database
// records as empty strings. Later, we'll
// turn them into arrays for better performance
$timestamp = ""; $temperature = ""; $humidity = "";
while($row = mysqli_fetch_array($mysql_result, MYSQLI_ASSOC)) {
$timestamp[] = $row["timestamp"];
$temperature[] = $row["temperature"];
$humidity[] = $row["humidity"];
}
$pchart_data->addPoints($timestamp,"Timestamp");
$pchart_data->addPoints($temperature,"Temperature");
$pchart_data->addPoints($humidity,"Humidity");
// Put the table column on the appropriate axis
$pchart_data->setAbscissa("Timestamp");
$pchart_data->setSerieOnAxis("Humidity", 1);
$pchart_data->setXAxisName("Time");
$pchart_data->setXAxisDisplay(AXIS_FORMAT_TIME,"H:i");
// Dedicate the first and second axis to
// Temperature and Humidity.
$pchart_data->setAxisName(0, "Temperature");
$pchart_data->setAxisUnit(0, "°C");
$pchart_data->setAxisName(1, "Humidity");
$pchart_data->setAxisUnit(0, "%");
// Create the pChart Image. The first two argument
// to the pImage object are the width and height
// of the rendered chart.
$pchart_image = new pImage(500, 300, $pchart_data);
// Set the font.
$pchart_image->setFontProperties(
["FontName" => PCHART_PATH . "/fonts/verdana.ttf",
"FontSize"=> 11]
);
// Set the graph area.
$pchart_image->setGraphArea(55,25, 475,275);
$pchart_image->drawScale();
$pchart_image->drawBarChart();
// Draw the chart as a stroke.
$pchart_image->Stroke();
?>
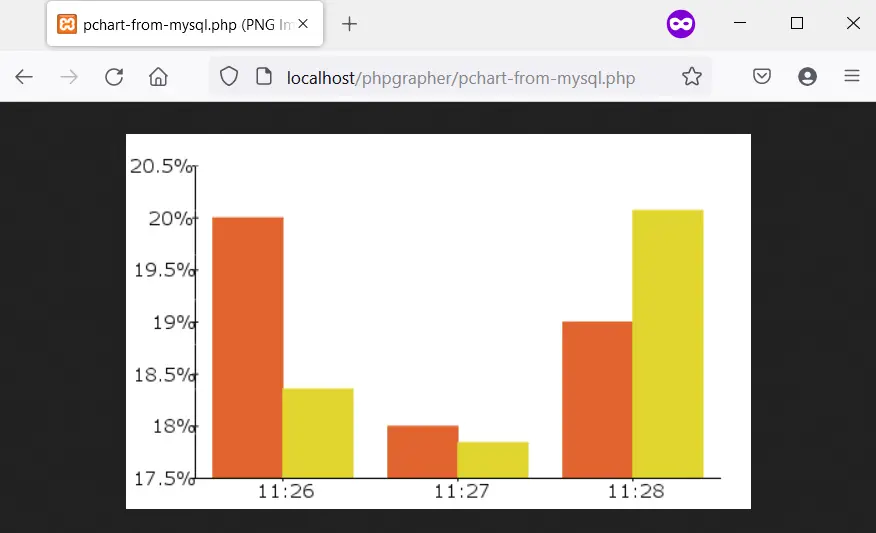
输出(你的时间会有所不同):
Habdul Hazeez is a technical writer with amazing research skills. He can connect the dots, and make sense of data that are scattered across different media.
LinkedIn