如何在 Matplotlib 直方图中手动设置 bin 的大小
Suraj Joshi
2024年2月15日
要绘制直方图,我们使用 hist2d() 函数,其中将 bin (箱数)n 作为参数传递。我们可以通过计算所需的箱数来设置箱的大小,以保持所需的大小。
将 bin 边界作为 hist() 函数的参数
hist 函数的语法:
hist(x,
bins: NoneType=None,
range: NoneType=None,
density: NoneType=None,
weights: NoneType=None,
cumulative: bool=False,
bottom: NoneType=None,
histtype: str=builtins.str,
align: str=builtins.str,
orientation: str=builtins.str,
rwidth: NoneType=None,
log: bool=False,
color: NoneType=None,
label: NoneType=None,
stacked: bool=False,
normed: NoneType=None,
data: NoneType=None,
**kwargs)
为了在 Matplotlib 中设置 bin 的大小,我们传递一个带有 bin 边界而不是 bin 数量的列表作为 bin 参数。
import numpy as np
import numpy.random as random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
data = np.random.random_sample(100) * 100.0
plt.hist(data, bins=[0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 80, 100])
plt.xlabel("Value")
plt.ylabel("Counts")
plt.title("Histogram Plot of Data")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
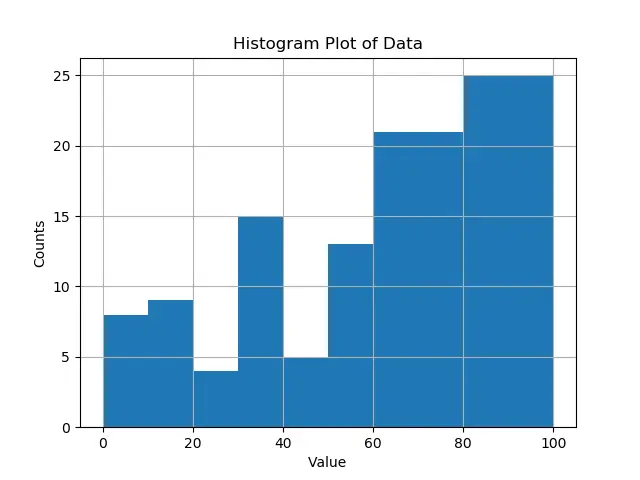
在上面的示例中,我们手动设置 bin 边界,并间接设置 bin 的宽度。我们也可以使用 np.arange 找到等距的边界。
为了使 bin 等距分布,我们可以使用 np.arange 查找等距边界。
import numpy as np
import numpy.random as random
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
binwidth = 10
data = np.random.random_sample(100) * 100.0
plt.hist(data, bins=np.arange(min(data), max(data) + binwidth, binwidth))
plt.xlabel("Data")
plt.ylabel("Counts")
plt.title("Histogram Plot of Data")
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
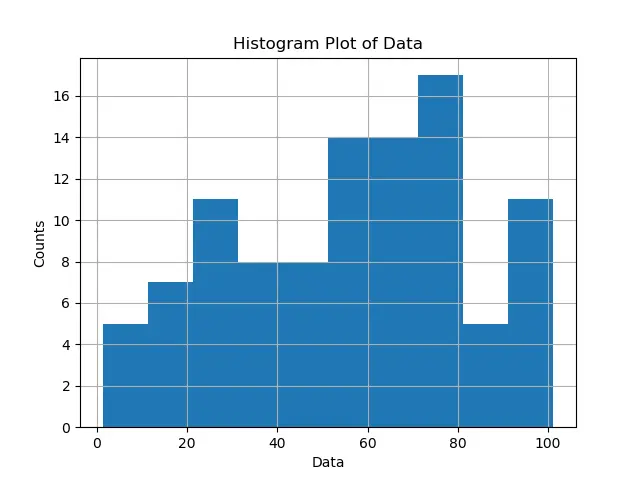
警告
np.arange 的第二个参数应该是 max(data) + binwidth,而不是 max(data),因为 np.arange(start, top, step) 创建的间隔包括 start,但是不包含 end。因此,我们需要在 max(data) 上添加区间 binwidth,以使实际停止为 max(data)。从所需宽度计算 bin 的数量(箱数)
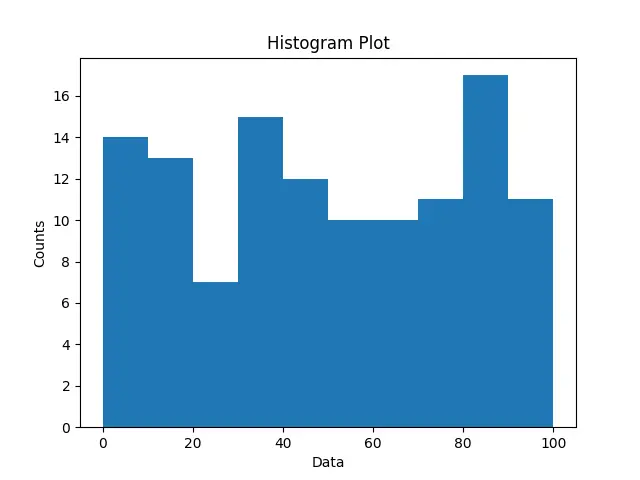
为了找到 bin 的数量,我们计算最大值和最小值之间的差除以所需的 bin(箱)宽度。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def find_bins(observations, width):
minimmum = np.min(observations)
maximmum = np.max(observations)
bound_min = -1.0 * (minimmum % width - minimmum)
bound_max = maximmum - maximmum % width + width
n = int((bound_max - bound_min) / width) + 1
bins = np.linspace(bound_min, bound_max, n)
return bins
data = np.random.random_sample(120) * 100
bins = find_bins(data, 10.0)
plt.hist(data, bins=bins)
plt.xlabel("Data")
plt.ylabel("Counts")
plt.title("Histogram Plot")
plt.show()
作者: Suraj Joshi
Suraj Joshi is a backend software engineer at Matrice.ai.
LinkedIn