检查 Bash 中的变量是否为空
-
使用
-z选项检查 Bash 中的变量是否为空 -
在 Bash 中使用
-n选项来检查变量是否为空 - 检查 Bash 中的变量是否为空 - 与空字符串比较
- 检查 Bash 中的变量是否为空 - 使用替换方法检查

本教程说明了使用带有 -z 和 -n 选项的 test 命令在 bash 中检查变量是否为空。
使用 -z 选项检查 Bash 中的变量是否为空
我们使用带有 -z 选项的 test 命令。 -z 选项检查字符串变量的长度是否为 0。
如果字符串变量的长度为 0,则测试返回 true,并且脚本将字符串变量为空输出到标准输出。如果字符串变量的长度不是 0,脚本会打印出字符串变量不为空。
在下面的例子中,greet 变量有一个分配给它的字符串。在测试过程中,检查 greet 变量存储的字符串值的长度是否为 0。
由于 greet 变量有字符串 Hi,它分配了两个字符,测试返回 false,并且脚本在标准输出中打印 greet 变量不为空。
greet='Hi'
if [ -z "$greet" ]
then
echo "\$greet is empty"
else
echo "\$greet is not empty"
fi
输出:
$greet is not empty
greet 变量在下面的脚本中被分配给一个空字符串。使用 test/[ 命令检查 greet 变量以查看其字符串值的长度是否为 0。
由于 greet 变量被分配给一个空字符串,测试返回 true,并且脚本打印到标准输出 greet 变量为空。
#!/bin/bash
greet=''
if [ -z "$greet" ]
then
echo "\$greet is empty"
else
echo "\$greet is not empty"
fi
输出:
$greet is empty
在 Bash 中使用 -n 选项来检查变量是否为空
下面的脚本使用带有 -n 选项的 test 命令来检查字符串变量是否为空。 -n 选项检查字符串变量中值的长度是否为非零。
如果变量中字符串的长度不为零,则测试返回 true,并打印出该变量不为空。如果字符串变量的长度为零,则测试返回 false,并打印出该变量为空。
greet 变量在下面的脚本中被分配给一个空字符串。当使用 test 命令检查 greet 变量时,如果它存储的字符串的长度不为零,则返回 false,并且脚本执行 else 部分中的命令。
#!/bin/bash
greet=''
if [ -n "$greet" ]
then
echo "\$greet is not empty"
else
echo "\$greet is empty"
fi
输出:
$greet is empty
greet 变量已分配给 Hi,这是一个在下面的脚本中包含两个字符的字符串。
检查 greet 变量中的字符串长度是否为非零的测试返回 true,因为 greet 变量被分配给具有两个字符的字符串。该脚本在标准输出中打印出 greet 变量不为空。
#!/bin/bash
greet='Hi'
if [ -n "$greet" ]
then
echo "\$greet is not empty"
else
echo "\$greet is empty"
fi
输出:
$greet is not empty
检查 Bash 中的变量是否为空 - 与空字符串比较
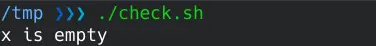
我们可以通过将其与""进行比较来检查该值是否为空。
x="Non-empty variable"
if [[ "$x" == "" ]]; then
echo "x is empty"
else
echo "x is not empty"
fi
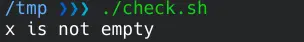
检查 Bash 中的变量是否为空 - 使用替换方法检查
如果定义了 x,则表达式被替换为 test,否则为 null。
if [ ${x:+test} ]; then
echo "x is not empty"
else
echo "x is empty"
fi