在 JavaScript 中调用 API
Mehvish Ashiq
2024年2月15日
API 代表应用程序编程接口,这意味着它是用于开发和集成不同软件应用程序的协议和定义的集合。
API 是一种在各种接口之间以及从服务器实时发送和获取信息或向服务器发送数据的方法。
在 JavaScript 中使用 Getuser() 函数调用和获取 API 的响应
我们将使用公共 API 并将 URL 保存在 api_url 变量中。你可以参考更多公共 API 此处。
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0" />
</head>
<body>
<div class="content">
<div class="details">
<h2>Random User's Details</h2>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Full Name</td>
<td><span id="fullname"></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Age</td>
<td><span id="age"></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Gender</td>
<td><span id="gender"></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Location</td>
<td><span id="location"></span></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Country</td>
<td><span id="country"></span></td>
</tr>
</table>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
.content {
text-align: center;
padding: 30px;
margin: 0px auto;
}
.details {
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
}
table,
td {
border-collapse: collapse;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
text-align: center;
padding: 10px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
const api_url = 'https://randomuser.me/api/';
async function getUser() {
// making a call to API
const response = await fetch(api_url);
// converting it to JSON format
const data = await response.json();
// getting data/information from JSON
const user = data.results[0];
let {first, last} = user.name;
let {gender, email, phone} = user;
let age = user.dob.age;
let {city, state, country} = user.location;
let fullName = first + ' ' + last;
// getting access to the span container
document.querySelector('#fullname').textContent = fullName;
document.querySelector('#age').textContent = age;
document.querySelector('#gender').textContent = gender;
document.querySelector('#location').textContent = city + ', ' + state;
document.querySelector('#country').textContent = country;
}
// Calling the getUser() function
getUser();
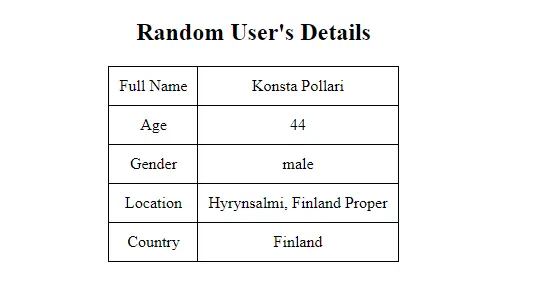
要检查输出,我们可以在 Google Chrome 和 Edge 中按 Ctrl+Shift+J 或右键单击打开控制台窗口-> 检查 -> 控制台。
输出:
注意
你可能会获得不同用户的详细信息,因为每次运行代码时,我们都会获得一个随机用户。
我们可以使用 async 和 await 确保即使在页面完全加载后信息仍然可见。
Async 和 await 用于异步编程。Async 总是确保返回 Promise,因为它总是返回值。
而且,如果没有,那么 JavaScript 会立即将其包装在一个 Promise 中,并使用它的值来解决。我们使用 await 函数来等待 Promise。
这只能在 async 块中使用。await 函数使 async 块等待直到 Promise 返回结果。
fetch() 方法将 URL 作为参数并通过网络异步获取所需的资源。
在 JavaScript 中创建另一个 API 以发送 POST 请求
const api_url = 'https://httpbin.org/post';
async function getUser() {
const response = await fetch(api_url, {
method: 'POST',
headers: {'Accept': 'application/json', 'Content-Type': 'application/json'},
body: JSON.stringify({
fullname: 'Thomas John',
age: 33,
gender: 'male',
location: 'Miam',
country: 'USA'
})
});
const data = await response.json();
console.log(data);
}
// Calling the function
getUser();
此方法返回的结果称为 response。我们使用 response.json() 将此响应解析为 JSON。
我们从 JSON 中检索数据/信息,并使用解构赋值将其保存在不同的变量中。之后,我们可以访问 <span> 容器并修改它们的 textContent。
输出(JSON):
{
args: { ... },
data: "{\"fullname\":\"Thomas John\",\"age\":33,\"gender\":\"male\",\"location\":\"Miam\",\"country\":\"USA\"}",
files: { ... },
form: { ... },
headers: {
Accept: "application/json",
Accept-Encoding: "gzip, deflate, br",
Accept-Language: "en-GB,en-US;q=0.9,en;q=0.8,ur;q=0.7",
Content-Length: "85",
Content-Type: "application/json",
Host: "httpbin.org",
Origin: "https://fiddle.jshell.net",
Referer: "https://fiddle.jshell.net/",
Sec-Ch-Ua: "\" Not A;Brand\";v=\"99\", \"Chromium\";v=\"98\", \"Google Chrome\";v=\"98\"",
Sec-Ch-Ua-Mobile: "?0",
Sec-Ch-Ua-Platform: "\"Windows\"",
Sec-Fetch-Dest: "empty",
Sec-Fetch-Mode: "cors",
Sec-Fetch-Site: "cross-site",
User-Agent: "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/98.0.4758.82 Safari/537.36",
X-Amzn-Trace-Id: "Root=1-6207e40f-1146923e2704c7e8542bf54e"
},
json: {
age: 33,
country: "USA",
fullname: "Thomas John",
gender: "male",
location: "Miam"
},
origin: "119.153.33.34",
url: "https://httpbin.org/post"
}
我们使用 JSON.stringify() 转换为字符串,因为 body 的值只能是字符串或对象。
作者: Mehvish Ashiq
