Java 锯齿状数组

本教程介绍了 Java 锯齿状数组。我们将通过不同的代码示例了解它的内存表示和实现。
Java 锯齿状数组
要理解锯齿状数组,你必须对数组有一个很好的理解。锯齿状数组,也称为不规则数组,是一个数组,其中每个成员数组的大小都不同。
这里,数组数组是指二维数组;它可以是 2D 或 3D 或更多维度。请参阅以下视觉演示以了解锯齿状数组。
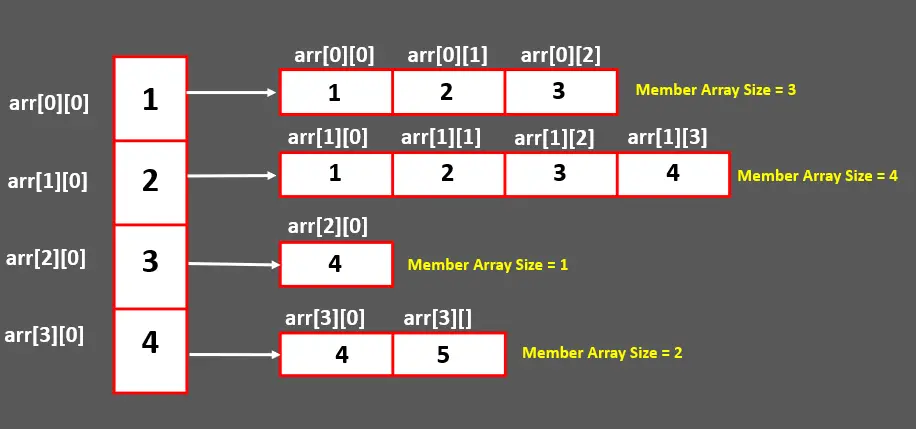
我们可以看到每个成员数组的大小互不相同。这就是我们所说的锯齿状或锯齿状数组。
Java 中锯齿状数组的声明与初始化
有多种方式来声明和初始化锯齿状数组;我们将在下面使用从视觉解释中提取的 int 类型数组来查看它们中的每一个。
使用第一种方法,我们首先通过指定大小来声明基本数组。然后,我们为每个成员数组写入不同的大小。
在这里,我们将声明和初始化过程分开。请参阅以下代码段。
声明锯齿状数组:
// declare base array of size 4 (it would be an array of arrays)
int arr[][] = new int[4][];
// declare member arrays
arr[0] = new int[3]; // here the 3 shows the no of columns in row-1
arr[1] = new int[4]; // here the 4 shows the no of columns in row-2
arr[2] = new int[1]; // here the 1 shows the no of columns in row-3
arr[3] = new int[2]; // here the 2 shows the no of columns in row-4
接下来,静态初始化锯齿状数组。
arr[0] = new int[] {1, 2, 3};
arr[1] = new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4};
arr[2] = new int[] {4};
arr[3] = new int[] {4, 5};
或者,我们可以动态初始化锯齿状数组,这意味着我们从用户那里获取输入并在运行时初始化数组。
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int base = 0; base < arr.length; base++) {
for (int member = 0; member < arr[base].length; member++) {
arr[base][member] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
在第二种方法中,我们可以一步声明和初始化锯齿状数组。我们可以用各种方式编写这一步。
请参阅下面给出的代码片段。
int arr[][] =
new int[][] {new int[] {1, 2, 3}, new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[] {4}, new int[] {4, 5}};
OR
int[][] arr = {new int[] {1, 2, 3}, new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[] {4}, new int[] {4, 5}};
OR
int[][] arr = {{1, 2, 3}, {1, 2, 3, 4}, {4}, {4, 5}};
让我们深入了解锯齿状数组的更详细实现,我们将在其中静态和动态地分配值。
Java 中的锯齿状数组实现示例
示例代码(锯齿状数组是静态初始化的):
public class jagggedArrayTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int arr[][] =
new int[][] {new int[] {1, 2, 3}, new int[] {1, 2, 3, 4}, new int[] {4}, new int[] {4, 5}};
for (int base = 0; base < arr.length; base++) {
System.out.print("arr[" + base + "] ======> {");
for (int member = 0; member < arr[base].length; member++) {
if (member < arr[base].length - 1)
System.out.print(arr[base][member] + ", ");
else
System.out.print(arr[base][member]);
}
System.out.print("}");
System.out.println();
}
}
}
输出:
arr[0] ======> {1, 2, 3}
arr[1] ======> {1, 2, 3, 4}
arr[2] ======> {4}
arr[3] ======> {4, 5}
我们首先在 main 函数中声明并初始化锯齿状数组。然后,我们使用嵌套的 for 循环来打印锯齿状数组,其中外循环用于迭代基本数组(行),而内循环用于迭代成员数组(列)。
示例代码(动态填充锯齿状数组):
import java.util.Scanner;
public class jaggedArrayTest {
/*
this function prints the populated jagged array
*/
static void printJaggedArray(int[][] arr) {
System.out.println("The populated array looks like as follows:");
for (int base = 0; base < arr.length; base++) {
System.out.print("arr[" + base + "] ======> {");
for (int member = 0; member < arr[base].length; member++) {
if (member < arr[base].length - 1)
System.out.print(arr[base][member] + ", ");
else
System.out.print(arr[base][member]);
}
System.out.print("}");
System.out.println();
}
}
/*
this function populates the jagged array by
taking input from the user
*/
static void populateJaggedArray(int[][] arr) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int base = 0; base < arr.length; base++) {
System.out.println("Enter the member array at index " + base);
for (int member = 0; member < arr[base].length; member++) {
arr[base][member] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// print jagged array
printJaggedArray(arr);
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
// declare base array of size 4 (it would be an array of arrays)
int arr[][] = new int[4][];
// declare member arrays
arr[0] = new int[3]; // here the 3 shows the no of columns in row-1
arr[1] = new int[4]; // here the 4 shows the no of columns in row-2
arr[2] = new int[1]; // here the 1 shows the no of columns in row-3
arr[3] = new int[2]; // here the 2 shows the no of columns in row-4
// populate jagged array
populateJaggedArray(arr);
}
}
输出:
Enter the member array at index 0
1 2 3
Enter the member array at index 1
1 2 3 4
Enter the member array at index 2
4
Enter the member array at index 3
4 5
The populated array looks like as follows:
arr[0] ======> {1, 2, 3}
arr[1] ======> {1, 2, 3, 4}
arr[2] ======> {4}
arr[3] ======> {4, 5}
在这里,我们在 jaggedArrayTest 类中拥有三个名为 main()、populateJaggedArray() 和 printJaggedArray() 的方法。main() 方法声明并初始化锯齿状数组,该数组被传递给 populateJaggedArray() 函数以进行填充。
此外,它调用 printJaggedArray() 来打印填充的锯齿状数组。请记住,我们只是动态地填充锯齿状数组,但你也可以使用用户的输入值来获取基本数组和成员数组的大小。
