在 Angular 中上传图片
- 在 Angular 中上传图片
- 在 Angular 中导出组件和声明变量
- Angular 中多个图像的基本上传
- Angular 中单个图像的基本上传
- Angular 中多个图像的上传和进度
- Angular 中单个图像的上传和进度
- 在 Angular 中调用上传函数

本文介绍以下内容:
- 使用 Angular 上传四种不同风格的图片。
- 图片上传时显示进度条。
- 上传完成后显示图片上传完成信息。
在 Angular 中上传图片
图像是任何 Web 应用程序的基本组成部分,每个网站都有图像。在本教程中,我们将学习如何以不同的方式在 Angular 中上传图像。
让我们使用以下命令创建一个新应用程序。
# angular
ng new my-app
在 Angular 中创建我们的新应用程序后,我们将使用此命令转到我们的应用程序目录。
# angular
cd my-app
现在,让我们运行我们的应用程序来检查所有依赖项是否安装正确。
# angular
ng serve --open
我们将为文件上传器导入库并设置组件。
# angular
import { Component, VERSION } from '@angular/core';
import {HttpClientModule, HttpClient, HttpRequest, HttpResponse, HttpEventType} from '@angular/common/http';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<input type="file" accept=".jpg,.png" class="button" (change)="upload($event.target.files)" />
<p>Upload Percent: {{percentDone}}% </p> <br />
<ng-container *ngIf="uploadSuccess" class="success">
<p class="sucess">Upload Successful</p>
</ng-container>
`,
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'],
})
在 Angular 中导出组件和声明变量
我们将导出我们的 AppComponent 并将变量 percentDone 声明为 number 和 UploadSuccess 作为 boolean。我们还将声明一个构造函数,它调用 HttpClient。
# angular
export class AppComponent {
percentDone: number;
uploadSuccess: boolean;
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {}
Angular 中多个图像的基本上传
Angular 中有 4 种不同风格的图片上传;多张图片的基本上传就是其中之一。可以以这种样式上传多张图片,而不显示图片的进度条。
basicUploadImage(files: File[]) {
var formData = new FormData();
Array.from(files).forEach((f) => formData.append('file', f));
this.http.post('https://file.io', formData).subscribe((event) => {
console.log('done');
});
}
我们正在向 https://file.io 发送上传请求,可以使用后端服务器 URL 进行更改。后端服务器将接收上传的图像数据,将发送一个 URL 到上传的文件。
Angular 中单个图像的基本上传
在 Angular 中上传图片的第二种方式是图片文件的基本上传。在这种风格中,用户一次只能上传一张图片。
上传图像时,此样式也不会显示进度。
basicUploadSingleImage(file: File) {
this.http.post('https://file.io', file).subscribe((event) => {
console.log('done');
});
}
Angular 中多个图像的上传和进度
在 Angular 中上传图片的第三种方式是上传多张图片的进度。用户可以上传多张图片,进度条显示以这种风格上传的百分比。
uploadImageAndProgress(files: File[]) {
console.log(files);
var formData = new FormData();
Array.from(files).forEach((f) => formData.append('file', f));
this.http.post('https://file.io', formData, {
reportProgress: true,
observe: 'events',
})
.subscribe((event) => {
if (event.type === HttpEventType.UploadProgress) {
this.percentDone = Math.round((100 * event.loaded) / event.total);
} else if (event instanceof HttpResponse) {
this.uploadSuccess = true;
}
});
}
Angular 中单个图像的上传和进度
在 Angular 中上传图片的第四种风格是带有进度条的单张图片。用户可以上传带有进度条的单个图像,显示以这种样式上传的百分比。
uploadAndProgressSingleImage(file: File) {
this.http
.post('https://file.io', file, {
reportProgress: true,
observe: 'events',
})
.subscribe((event) => {
if (event.type === HttpEventType.UploadProgress) {
this.percentDone = Math.round((100 * event.loaded) / event.total);
} else if (event instanceof HttpResponse) {
this.uploadSuccess = true;
}
});
}
在 Angular 中调用上传函数
我们在 Angular 中添加了四个上传功能;我们可以使用所需的样式调用我们的上传函数。
uploadImage(files: File[]) {
this.uploadImageAndProgress(files);
}
输出:
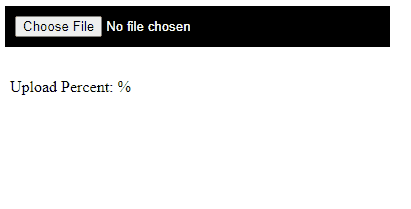
概括
我们讨论了 Angular 中四种不同风格的图片上传,以及如何在我们的 upload 函数中调用它们。完整的代码如下。
import { Component, VERSION } from '@angular/core';
import {
HttpClientModule,
HttpClient,
HttpRequest,
HttpResponse,
HttpEventType,
} from '@angular/common/http';
@Component({
selector: 'my-app',
template: `
<input type="file" accept=".jpg,.png" class="button" (change)="uploadImage($event.target.files)" />
<p>Upload Percent: {{percentDone}}% </p> <br />
<ng-container *ngIf="uploadSuccess" class="success">
<p class="sucess">Upload Successful</p>
</ng-container>
`,
styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'],
})
export class AppComponent {
percentDone: number;
uploadSuccess: boolean;
constructor(private http: HttpClient) {}
uploadImage(files: File[]) {
this.uploadImageAndProgress(files);
}
basicUploadImage(files: File[]) {
var formData = new FormData();
Array.from(files).forEach((f) => formData.append('file', f));
this.http.post('https://file.io', formData).subscribe((event) => {
console.log('done');
});
}
basicUploadSingleImage(file: File) {
this.http.post('https://file.io', file).subscribe((event) => {
console.log('done');
});
}
uploadImageAndProgress(files: File[]) {
console.log(files);
var formData = new FormData();
Array.from(files).forEach((f) => formData.append('file', f));
this.http.post('https://file.io', formData, {
reportProgress: true,
observe: 'events',
})
.subscribe((event) => {
if (event.type === HttpEventType.UploadProgress) {
this.percentDone = Math.round((100 * event.loaded) / event.total);
} else if (event instanceof HttpResponse) {
this.uploadSuccess = true;
}
});
}
uploadAndProgressSingleImage(file: File) {
this.http
.post('https://file.io', file, {
reportProgress: true,
observe: 'events',
})
.subscribe((event) => {
if (event.type === HttpEventType.UploadProgress) {
this.percentDone = Math.round((100 * event.loaded) / event.total);
} else if (event instanceof HttpResponse) {
this.uploadSuccess = true;
}
});
}
}
Rana is a computer science graduate passionate about helping people to build and diagnose scalable web application problems and problems developers face across the full-stack.
LinkedIn