資料淺/深拷貝
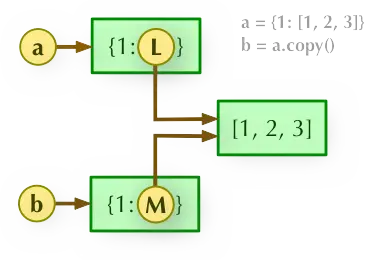
資料拷貝有兩種,淺拷貝(shallow copy)以及深拷貝(deep copy)。從名字上可以看出來,淺拷貝,僅拷貝指向物件的指標;而深拷貝,是將整個物件拷貝到另外一塊記憶體中。
淺拷貝
比如,我們有一個列表 [1, [1,2,3]],淺拷貝的話,列表中的第二個元素-列表 [1,2,3] 假如發生變化的話,它會同時在原始列表,以及淺拷貝後的列表做相同的改變,因為它們指向的是同一個記憶體地址。
A = [1, [1, 2, 3]]
B = A.copy()
A[1].append(4)
print(B)
# Out: [1, [1,2,3,4]]
print(A)
# Out: [1, [1,2,3,4]]
A[1] is B[1]
# Out: True

淺拷貝有兩種實現方式,一個是用 copy() 方法,另外一個可以用 copy 模組裡面的 copy 函式。
列表型別還有一種淺拷貝方法,就是通過切片來生成的新列表,也是淺拷貝的結果。
A = [1, [1, 2, 3]]
B = A[:]
B[1] is A[1]
# Out: True
深拷貝
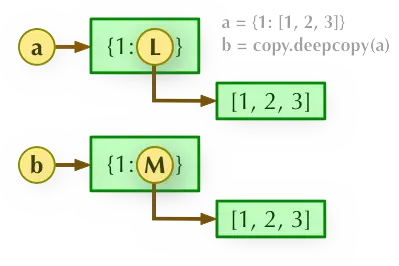
深拷貝是完全的將被拷貝物件資料拷貝到新的記憶體中,新舊兩個資料物件地址完全不同,它們是 100%獨立的資料。
import copy
A = [1, [1, 2, 3]]
B = copy.deepcopy(A)
A is B
# Out: False
A[1].append(4)
print(A, B)
# Out: [1, [1, 2, 3, 4]] [1, [1, 2, 3]]
A[1] is B[1]
Founder of DelftStack.com. Jinku has worked in the robotics and automotive industries for over 8 years. He sharpened his coding skills when he needed to do the automatic testing, data collection from remote servers and report creation from the endurance test. He is from an electrical/electronics engineering background but has expanded his interest to embedded electronics, embedded programming and front-/back-end programming.
LinkedIn