在 Python 中讀取二進位制檔案
-
用 Python 中的
open()函式讀取一個二進位制檔案 -
用 Python 中的
pathlib.Path讀取二進位制檔案 -
用 Python 中的
numpy.fromfile()函式讀取一個二進位制檔案

程式或內部處理器對二進位制檔案進行解釋。它包含位元組作為內容。當我們讀取一個二進位制檔案時,會返回一個型別為 bytes 的物件。
用 Python 中的 open() 函式讀取一個二進位制檔案
在 Python 中,我們有 open() 函式,用來建立一個檔案物件,將檔案的路徑傳給函式,並以特定的模式開啟檔案,預設為讀模式。當我們開啟二進位制檔案時,在以讀、寫或追加模式開啟此類檔案時,必須指定 b 引數。在本教程中,我們將處理二進位制讀取模式-rb。
在下面的程式碼中,我們將讀取一個二進位制檔案並從檔案中列印一個字元。
with open("sample.bin", "rb") as f:
data = f.read()
print(data[2])
輸出:
83
如果我們列印單個字元,那麼我們可以檢視整數。
Python 有一個名為 struct 的包,它有很多方法,可以用來處理儲存在檔案、資料庫等資源中的二進位制資料。
struct.unpack() 用來讀取打包後的資料,以指定的格式佈局。這種佈局在打包和解壓資料時使用,是用格式字元指定的。這些格式字元以及它們的大小如下所示。
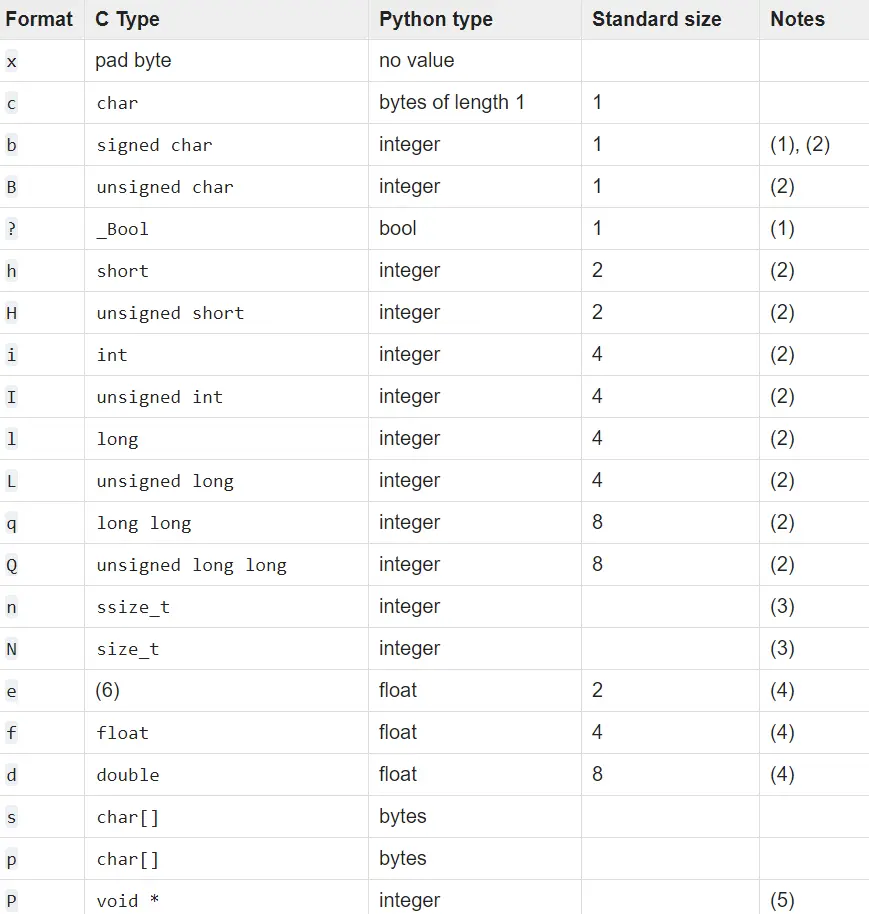
請注意,struct.unpack() 函式總是返回一個元組。
import struct
with open("sample.bin", "rb") as f:
data = f.read()
unpack_result = struct.unpack("hhl", data[0:8])
print(unpack_result)
輸出:
(1280, 27731, 7037801)
這裡,hhl 表示短,短,長 int 作為資料格式佈局,我們可以在輸出中看到。這就是為什麼解包的緩衝區只有 8 個位元組,因為格式佈局的大小是 8(2+2+4)。
用 Python 中的 pathlib.Path 讀取二進位制檔案
我們也可以使用 pathlib 庫中 Path 類中的 read_bytes() 方法,以位元組模式讀取檔案,然後使用 struct.unpack() 函式解釋資料,如前所述。
from pathlib import Path
import struct
data = Path("sample.bin").read_bytes()
multiple = struct.unpack("ii", data[:8])
print(multiple)
輸出:
(1817380096, 7037801)
用 Python 中的 numpy.fromfile() 函式讀取一個二進位制檔案
NumPy 模組中提供了另一種有趣的方法。使用該模組中的 fromfile() 函式,我們可以在使用 dtype() 函式指定格式資料後,從檔案中讀取二進位制資料。這被認為是一種快速的方法。下面的程式碼展示瞭如何實現這個功能。
import numpy as np
with open("sample.bin") as f:
rectype = np.dtype(np.int32)
bdata = np.fromfile(f, dtype=rectype)
print(bdata)
輸出:
[1817380096 7037801]
在這裡,我們將格式型別指定為 32 位整數,並使用 fromfile() 函式提取資料。
Manav is a IT Professional who has a lot of experience as a core developer in many live projects. He is an avid learner who enjoys learning new things and sharing his findings whenever possible.
LinkedIn