在 PowerShell 中使用 CmdletBinding 屬性
-
PowerShell 中的
CmdletBinding屬性 -
將
CmdletBinding屬性與Verbose引數一起使用 -
將
CmdletBinding屬性與$PSCmdlet物件和SupportsShouldProcess一起使用 -
使用
CmdletBinding屬性和Parameter屬性來控制函式引數

cmdlet 是在 PowerShell 環境中執行單一功能的輕量級指令碼。cmdlet 可以用任何 .Net 語言編寫。
通常,cmdlet 表示為執行命令的動詞-名詞對。該命令是對底層作業系統的命令,以由終端使用者執行特定服務。
PowerShell 環境包括 200 多個基本的 cmdlet,例如 New-Item、Move-Item、Set-Location 和 Get-Location。cmdlet 共享一組簡單的 PowerShell 函式中不可用的通用功能。
- 支援
-WhatIf、ErrorAction、Verbose等常用引數。 - 提示確認
- 強制引數支援
PowerShell 中的 CmdletBinding 屬性
通過繼承上面討論的基本 cmdlet 功能,可以將簡單的 PowerShell 函式編寫為高階函式。CmdletBinding 屬性使你能夠訪問這些基本的 cmdlet 功能。
下面顯示了帶有所有可能引數的 CmdletBinding 屬性語法。
{
[CmdletBinding(ConfirmImpact=<String>,
DefaultParameterSetName=<String>,
HelpURI=<URI>,
SupportsPaging=<Boolean>,
SupportsShouldProcess=<Boolean>,
PositionalBinding=<Boolean>)]
Param ($myparam)
Begin{}
Process{}
End{}
}
假設我們有一個名為 Helloworld-To-UpperCase 的簡單 PowerShell 函式。
Function Helloworld-To-UpperCase {
"helloworld".ToUpper();
}
此函式沒有附加引數。因此,這稱為簡單的 PowerShell 函式。
但是我們可以使用 CmdletBinding 屬性將此功能轉換為高階功能並訪問基本的 cmdlet 功能和引數,如下所示。
Function Helloworld-To-UpperCase {
[CmdletBinding()]Param()
"helloworld".ToUpper();
}
Helloworld-To-UpperCase 函式已轉換為繼承所有基本 cmdlet 功能的高階函式。基本的 cmdlet 引數可用於此函式。
如果你在 PowerShell 視窗中使用 - 呼叫此函式,它應該列出來自 cmdlet 的所有常用引數。
helloworld-to-uppercase -
輸出:
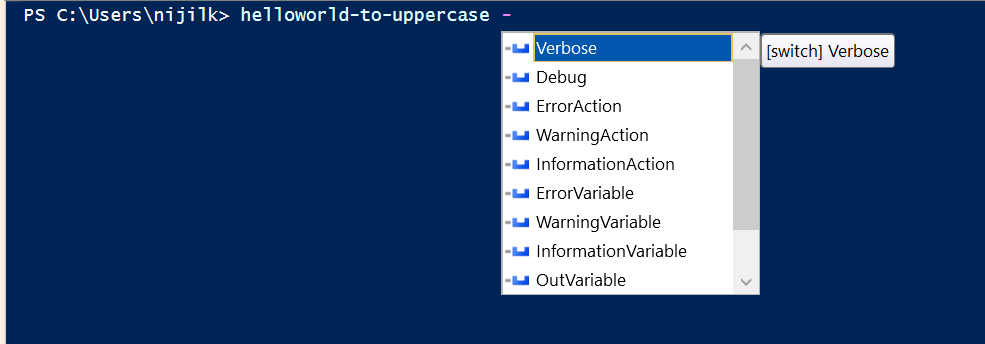
常見的 cmdlet 引數和功能可以在我們的高階功能中使用以擴充套件功能。
將 CmdletBinding 屬性與 Verbose 引數一起使用
-verbose 是有價值的常用引數之一,可以在執行高階功能時顯示訊息。
Function Helloworld-To-UpperCase {
[CmdletBinding()]Param()
Write-Verbose "This is the common parameter usage -Version within our Helloworld-To-UpperCase function"
"helloworld".ToUpper();
}
當我們使用 -verbose 引數呼叫上述函式時,它會將所有 Write-Verbose 字串列印到 PowerShell 視窗。
HelloWorld-To-UpperCase -Verbose
輸出:
將 CmdletBinding 屬性與 $PSCmdlet 物件和 SupportsShouldProcess 一起使用
由於我們使用了 CmdletBinding 屬性,我們的高階函式可以輕鬆訪問 $PSCmdlet 物件。該物件包含多個方法,例如 ShouldContinue、ShouldProcess、ToString、WriteDebug 等。
將 CmdletBinding 屬性與 ShouldContinue 方法一起使用
此方法允許使用者處理確認請求。同時,必須將 SupportsShouldProcess 引數設定為 $True。
ShouldContinue 方法有幾個過載方法,我們將使用帶有兩個引數的方法。
Function Helloworld-To-UpperCase {
[CmdletBinding(SupportsShouldProcess=$True)]Param()
Write-Verbose "This is the common parameter usage -Version within our Helloworld-To-UpperCase function"
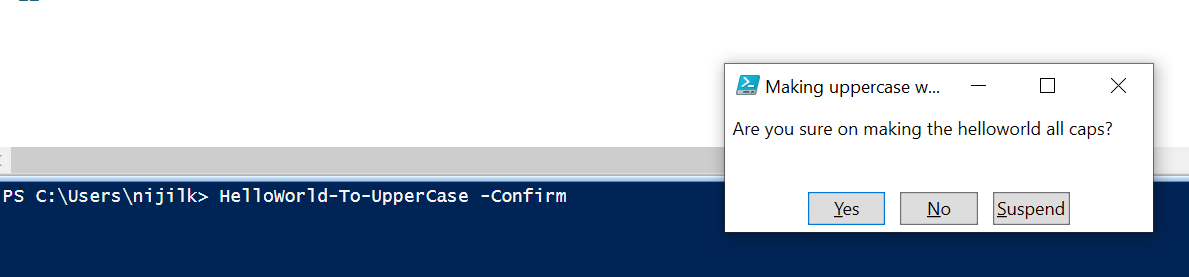
if ($PSCmdlet.ShouldContinue("Are you sure on making the helloworld all caps?", "Making uppercase with ToUpper")) {
"helloworld".ToUpper();
} Else {
"helloworld kept in lowercase."
}
}
我們可以使用 -Confirm 引數呼叫該函式,它會顯示一個確認框,如下所示。
HelloWorld-To-UpperCase -Confirm
輸出:
如果使用者點選 Yes,它應該實現 if 塊中的方法並以大寫字母列印 helloworld 字串。
如果不是,它應該顯示 helloworld 保持在小寫訊息。
使用 CmdletBinding 屬性和 Parameter 屬性來控制函式引數
讓我們讓我們的高階函式將一個引數作為一個字串。
Function Helloworld-To-UpperCase {
[CmdletBinding(SupportsShouldProcess=$True)]
Param([string]$word)
Write-Verbose "This is the common parameter usage -Version within our Helloworld-To-UpperCase function"
if ($PSCmdlet.ShouldContinue("Are you sure on making the helloworld all caps?", "Making uppercase with ToUpper")) {
$word.ToUpper();
} Else {
"helloworld kept in lowercase."
}
}
我們已將 Helloworld-To-UpperCase 函式更改為採用一個名為 $word 的字串型別引數。當函式被呼叫時,我們需要提供一個字串作為引數。
提供的文字將轉換為大寫。如果使用者沒有提供任何文字引數,該函式將給出一個空輸出。
我們可以通過強制 $word 引數並給引數位置 0 來控制這一點。
Function Helloworld-To-UpperCase {
[CmdletBinding(SupportsShouldProcess=$True)]
Param(
[Parameter(
Mandatory=$True, Position=0
) ]
[string]$word
)
#Verbose
Write-Verbose "This is the common parameter usage -Version within our Helloworld-To-UpperCase function"
#If/Else block for request processing
if ($PSCmdlet.ShouldContinue("Are you sure on making the helloworld all caps?", "Making uppercase with ToUpper")) {
$word.ToUpper();
} Else {
"helloworld kept in lowercase."
}
}
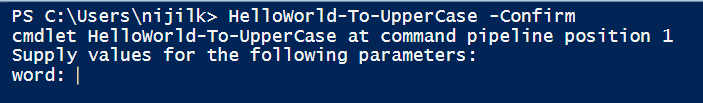
我們新增了一些標誌來控制 $word 引數的行為。由於它是強制性的,因此我們需要在函式執行時提供一個字串值。
HelloWorld-To-UpperCase -Confirm "stringtouppercase"
如果我們不提供 text 引數,PowerShell 會一直要求這樣做。
你可以使用多個標誌來控制函式中的引數,如以下 Parameter 屬性語法所示。
Param
(
[Parameter(
Mandatory=<Boolean>,
Position=<Integer>,
ParameterSetName=<String>,
ValueFromPipeline=<Boolean>,
ValueFromPipelineByPropertyName=<Boolean>,
ValueFromRemainingArguments=<Boolean>,
HelpMessage=<String>,
)]
[string[]]
$Parameter1
)
Nimesha is a Full-stack Software Engineer for more than five years, he loves technology, as technology has the power to solve our many problems within just a minute. He have been contributing to various projects over the last 5+ years and working with almost all the so-called 03 tiers(DB, M-Tier, and Client). Recently, he has started working with DevOps technologies such as Azure administration, Kubernetes, Terraform automation, and Bash scripting as well.