C++ 中的多重繼承
本文將演示有關如何在 C++ 中使用多重繼承的多種方法。
使用多重繼承將兩個給定類的多個屬性應用於另一個類
C++ 中的類可以具有多個繼承,這提供了從多個直接基類派生一個類的可能性。
這意味著如果沒有仔細實現這些類,則可能會出現特殊的異常行為。例如,考慮以下程式碼段程式碼,其中 C 類是從 B 和 A 類派生的。它們都有預設的建構函式,該建構函式輸出特殊的字串。雖然,當我們在 mainc 函式中宣告 C 型別的物件時,三個建構函式會列印輸出。請注意,建構函式以與繼承相同的順序被呼叫。另一方面,解構函式的呼叫順序相反。
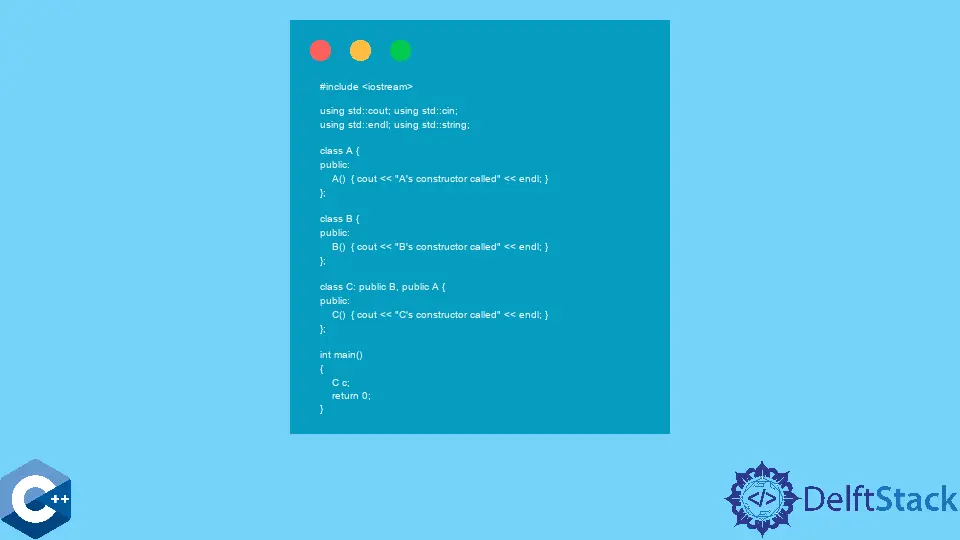
#include <iostream>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
class A {
public:
A() { cout << "A's constructor called" << endl; }
};
class B {
public:
B() { cout << "B's constructor called" << endl; }
};
class C : public B, public A {
public:
C() { cout << "C's constructor called" << endl; }
};
int main() {
C c;
return 0;
}
輸出:
Bs constructor called
As constructor called
Cs constructor called
使用 virtual 關鍵字修復基類的多個副本
請注意,以下程式輸出 Planet 類建構函式的兩個例項,分別是 Mars 和 Earth 建構函式,最後是 Rock 類建構函式。同樣,當物件超出範圍時,Planet 類的解構函式將被呼叫兩次。請注意,可以通過在 Mars 和 Earth 類中新增 virtual 關鍵字來解決此問題。當一個類具有多個基類時,有可能派生
類將從其兩個或多個基類繼承具有相同名稱的成員。
#include <iostream>
using std::cin;
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
class Planet {
public:
Planet(int x) { cout << "Planet::Planet(int ) called" << endl; }
};
class Mars : public Planet {
public:
Mars(int x) : Planet(x) { cout << "Mars::Mars(int ) called" << endl; }
};
class Earth : public Planet {
public:
Earth(int x) : Planet(x) { cout << "Earth::Earth(int ) called" << endl; }
};
class Rock : public Mars, public Earth {
public:
Rock(int x) : Earth(x), Mars(x) { cout << "Rock::Rock(int ) called" << endl; }
};
int main() { Rock tmp(30); }
輸出:
Planet::Planet(int ) called
Mars::Mars(int ) called
Planet::Planet(int ) called
Earth::Earth(int ) called
Rock::Rock(int ) called
Founder of DelftStack.com. Jinku has worked in the robotics and automotive industries for over 8 years. He sharpened his coding skills when he needed to do the automatic testing, data collection from remote servers and report creation from the endurance test. He is from an electrical/electronics engineering background but has expanded his interest to embedded electronics, embedded programming and front-/back-end programming.
LinkedIn